All Categories
Featured
Table of Contents
- – Geophysical Survey Methods in Alfred Cove Aus...
- – Geophysicist Education in Jandakot WA 2021
- – What Does A Geophysicist Do? in Wexcombe Wes...
- – Career Guide: Geophysicist in East Fremantl...
- – How To Become A Geophysicist in North Frema...
- – Geophysics in City Beach Western Australia...
- – Geophysicist in Como Oz 2021
- – An Assessment Of Geophysical Survey Techni...
- – How To Become A Geophysicist in Kelmscott ...
- – What Is Geophysics? in Brookdale Western A...
Geophysical Survey Methods in Alfred Cove Aus 2022
A geophysicist studies physical elements of the earth and utilizes intricate devices to collect information on earthquakes and seismic waves, which move through and around the earth. The finest industries for geophysicists are the mining and oil markets, as they play a big part in the acquisition of natural resources.
This Geophysicist task description example includes the list of most crucial Geophysicist responsibilities and obligations as shown below. It can be modified to fit the specific Geophysicist profile you're attempting to fill as a recruiter or task hunter.
Profession opportunities differ commonly throughout a series of fields including geophysical information, climate modelling, engineering geology, hydrology, mining, ecological consulting, natural deposits expedition, farming, and others. There are numerous profession paths that can combine your scholastic backgrounds, abilities, and experience with your different interests. Check out the task titles listed below for ideas.
Geophysicist Education in Jandakot WA 2021
Check out the National Occupational Classification website to research standard requirements and responsibilities of tasks in your field.
Geophysics plays in crucial role in many aspects of civil engineering, petroleum engineering, mechanical engineering, and mining engineering, along with mathematics, physics, geology, chemistry, hydrology, and computer technology. Therefore, students in other majors may consider a minor in geophysical engineering. The core courses needed for a minor are: GPGN229, Mathematical Geophysics (3.
0 credits) GPGN329, Physics of the Earth II (3. 0 credits) Students may satisfy the remaining 5 hours with a combination of other geophysics courses, as well as courses in geology, mathematics, or computer system science, depending on the student's major.
What Does A Geophysicist Do? in Wexcombe Western Australia 2021
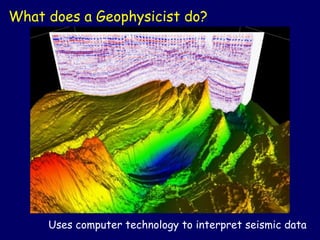
The salary level of geophysicists can differ depending on aspects such as their level of education, their level of experience, where they work, and many others. Some geophysicists may likewise invest long periods of time working in little groups in remote places.
When conducting fieldwork, the working hours of geophysicists can be long and include nights, weekends and holidays. To become a proficient geophysicist, you need to posses a specific set of abilities and personality type. These abilities and traits will allow you to efficiently perform the responsibilities of your job, as well as maintain a favorable mindset towards your work.
Career Guide: Geophysicist in East Fremantle WA 2020
Colleges and universities Federal, provincial/state federal government departments Oil, gas and mining business Non-profit companies Geological and geophysical consulting business Public and private research companies Our task board below has "Geophysicist" posts in Canada, the United States, the UK and Australia, when available:.
Our data shows that the greatest spend for a Geophysicist is $165k/ year Our data suggests that the most affordable spend for a Geophysicist is $55k/ year Increasing your pay as a Geophysicist is possible in various methods. Change of employer: Consider a career transfer to a new company that wants to pay higher for your skills.
Handling Experience: If you are a Geophysicist that oversees more junior Geophysicists, this experience can increase the likelihood to make more.
How To Become A Geophysicist in North Fremantle WA 2020
Physics of the Earth and its area Age of the sea flooring. Much of the dating details originates from magnetic anomalies. Geophysics () is a topic of natural science worried with the physical processes and physical properties of the Earth and its surrounding area environment, and making use of quantitative techniques for their analysis.
The term geophysics classically describes solid earth applications: Earth's shape; its gravitational, electromagnetic fields, and electro-magnetic fields; its internal structure and structure; its dynamics and their surface area expression in plate tectonics, the generation of magmas, volcanism and rock development. However, modern-day geophysics companies and pure scientists use a more comprehensive meaning that includes the water cycle consisting of snow and ice; fluid characteristics of the oceans and the atmosphere; electrical power and magnetism in the ionosphere and magnetosphere and solar-terrestrial physics; and analogous problems related to the Moon and other planets. To provide a clearer idea of what makes up geophysics, this area describes phenomena that are studied in physics and how they relate to the Earth and its environments. Geophysicists also investigate the physical procedures and residential or commercial properties of the Earth, its fluid layers, and electromagnetic field along with the near-Earth environment in the Planetary system, that includes other planetary bodies.
The gravitational pull of the Moon and Sun triggers two high tides and 2 low tides every lunar day, or every 24 hr and 50 minutes. There is a space of 12 hours and 25 minutes in between every high tide and between every low tide. Gravitational forces make rocks push down on deeper rocks, increasing their density as the depth boosts.
Geophysics in City Beach Western Australia 2020
The surface gravitational field offers details on the dynamics of tectonic plates. The geopotential surface called the geoid is one definition of the shape of the Earth. The geoid would be the international mean sea level if the oceans remained in balance and could be extended through the continents (such as with really narrow canals).
The main sources of heat are the primitive heat and radioactivity, although there are likewise contributions from phase shifts. Heat is mostly reached the surface by thermal convection, although there are 2 thermal boundary layers the coremantle boundary and the lithosphere in which heat is carried by conduction. Some heat is brought up from the bottom of the mantle by mantle plumes. If the waves come from a localized source such as an earthquake or surge, measurements at more than one location can be used to find the source. The places of earthquakes provide information on plate tectonics and mantle convection.
Comprehending their mechanisms, which depend on the type of earthquake (e. g., intraplate or deep focus), can lead to better price quotes of earthquake danger and enhancements in earthquake engineering. We mainly discover electrical energy during thunderstorms, there is always a down electrical field near the surface area that averages 120 volts per meter. A variety of electric methods are utilized in geophysical survey., a capacity that arises in the ground because of manufactured or natural disturbances.
Geophysicist in Como Oz 2021
In the highly conductive liquid iron of the outer core, magnetic fields are produced by electrical currents through electromagnetic induction.
In the core, they most likely have little observable effect on the Earth's magnetic field, however slower waves such as magnetic Rossby waves might be one source of geomagnetic nonreligious variation. Electromagnetic methods that are utilized for geophysical study consist of short-term electromagnetics, magnetotellurics, surface nuclear magnetic resonance and electro-magnetic seabed logging. , powering the geodynamo and plate tectonics.
An Assessment Of Geophysical Survey Techniques ... in Yokine Aus 2022
Radioactive aspects are used for radiometric dating, the main method for establishing an absolute time scale in geochronology. Unstable isotopes decay at predictable rates, and the decay rates of different isotopes cover a number of orders of magnitude, so radioactive decay can be used to accurately date both current events and events in past geologic periods.
Fluid movements occur in the magnetosphere, atmosphere, ocean, mantle and core. Even the mantle, though it has an enormous viscosity, streams like a fluid over long period of time periods. This circulation is shown in phenomena such as isostasy, post-glacial rebound and mantle plumes. The mantle flow drives plate tectonics and the flow in the Earth's core drives the geodynamo.
Waves and other phenomena in the magnetosphere can be modeled utilizing magnetohydrodynamics. The physical residential or commercial properties of minerals must be comprehended to infer the structure of the Earth's interior from seismology, the geothermal gradient and other sources of information. Mineral physicists study the flexible residential or commercial properties of minerals; their high-pressure stage diagrams, melting points and formulas of state at high pressure; and the rheological properties of rocks, or their ability to flow. The viscosity of rocks is impacted by temperature and pressure, and in turn, determines the rates at which tectonic plates move. Water is a really complex compound and its unique homes are important for life. Its physical residential or commercial properties shape the hydrosphere and are a vital part of the water cycle and environment.
How To Become A Geophysicist in Kelmscott WA 2022
The lots of types of rainfall include a complicated mix of procedures such as coalescence, supercooling and supersaturation. Some precipitated water ends up being groundwater, and groundwater flow includes phenomena such as percolation, while the conductivity of water makes electrical and electromagnetic techniques beneficial for tracking groundwater circulation. Physical residential or commercial properties of water such as salinity have a large impact on its movement in the oceans. The Earth is roughly spherical, but it bulges towards the Equator, so it is approximately in the shape of an ellipsoid (see Earth ellipsoid). This bulge is due to its rotation and is nearly constant with an Earth in hydrostatic balance. The in-depth shape of the Earth, however, is likewise affected by the distribution of continents and ocean basins, and to some extent by the characteristics of the plates.
(5. 515) is far higher than the typical particular gravity of rocks at the surface (2.
33 M R2, compared to 0. 4 M R2 for a sphere of consistent density). Some of the density increase is compression under the huge pressures inside the Earth.
What Is Geophysics? in Brookdale Western Australia 2022
The conclusion is that pressure alone can not account for the boost in density. Rather, we understand that the Earth's core is made up of an alloy of iron and other minerals. Restorations of seismic waves in the deep interior of the Earth reveal that there are no S-waves in the outer core.
The outer core is liquid, and the motion of this highly conductive fluid creates the Earth's field. Earth's inner core, however, is strong due to the fact that of the enormous pressure. Restoration of seismic reflections in the deep interior suggests some major discontinuities in seismic velocities that demarcate the major zones of the Earth: inner core, outer core, mantle, lithosphere and crust.
Table of Contents
- – Geophysical Survey Methods in Alfred Cove Aus...
- – Geophysicist Education in Jandakot WA 2021
- – What Does A Geophysicist Do? in Wexcombe Wes...
- – Career Guide: Geophysicist in East Fremantl...
- – How To Become A Geophysicist in North Frema...
- – Geophysics in City Beach Western Australia...
- – Geophysicist in Como Oz 2021
- – An Assessment Of Geophysical Survey Techni...
- – How To Become A Geophysicist in Kelmscott ...
- – What Is Geophysics? in Brookdale Western A...
Latest Posts
Geophysics, Engineering Geophysics And Applied ... in Carmel Western Australia 2023
Airborne Geophysical Surveys Of The Lower Mississippi ... in Balcatta Oz 2022
Working As A Geophysicist And Oceanographer In Canada in Cannington Australia 2023
More
Latest Posts
Geophysics, Engineering Geophysics And Applied ... in Carmel Western Australia 2023
Airborne Geophysical Surveys Of The Lower Mississippi ... in Balcatta Oz 2022
Working As A Geophysicist And Oceanographer In Canada in Cannington Australia 2023