All Categories
Featured
Table of Contents
- – Geophysicist Bob Embley: Ocean Exploration Ca...
- – Geophysical Survey - Plaza Of The Columns Co...
- – Geology Careers: Degree Requirements, Cost &...
- – Geophysical Methods Commonly Employed For G...
- – Geophysical Prospecting in Beckenham Oz 2020
- – Geophysicist Salary And Job Description 20...
- – Geophysical Survey in Lesmurdie Western Au...
- – Bs In Physics: Geophysics in Mt Helena Aus...
- – Geophysical Surveys - U.s. Geological Surv...
- – Geophysics in Woodvale WA 2023
Geophysicist Bob Embley: Ocean Exploration Careers in Nollamara WA 2023
What is the task description of a Geophysicist? What are the responsibilities and duties of a Geophysicist? What does a Geophysicist do? A geophysicist studies physical elements of the earth and uses complex devices to gather data on earthquakes and seismic waves, which move through and around the earth. The best industries for geophysicists are the mining and oil markets, as they play a substantial part in the acquisition of natural deposits.
This Geophysicist task description example includes the list of crucial Geophysicist duties and duties as shown below. It can be modified to fit the specific Geophysicist profile you're attempting to fill as a recruiter or job candidate.
Profession opportunities vary commonly throughout a variety of fields including geophysical data, environment modelling, engineering geology, hydrology, mining, environmental consulting, natural deposits exploration, agriculture, and others. There are many profession courses that can integrate your scholastic backgrounds, skills, and experience with your different interests. Read through the job titles listed below for ideas.
Geophysical Survey - Plaza Of The Columns Complex in Mosman Park Oz 2021
Check out the National Occupational Classification site to research study fundamental requirements and obligations of jobs in your field.
Geophysics plays in important role in lots of elements of civil engineering, petroleum engineering, mechanical engineering, and mining engineering, as well as mathematics, physics, geology, chemistry, hydrology, and computer technology. For that reason, students in other majors might think about a small in geophysical engineering. The core courses needed for a small are: GPGN229, Mathematical Geophysics (3.
0 credits) GPGN329, Physics of the Earth II (3. 0 credits) Trainees may please the remaining 5 hours with a mix of other geophysics courses, as well as courses in geology, mathematics, or computer science, depending on the student's significant.
Geology Careers: Degree Requirements, Cost & Salary in Yanchep Western Australia 2020

The wage level of geophysicists can vary depending on aspects such as their level of education, their level of experience, where they work, and many others. According to the 2018 Alberta Wage and Income Study, Albertans working in the occupational group make an average income of annually. According to Work, BC (the Province of British Columbia), the annual provincial mean salary of B.C.
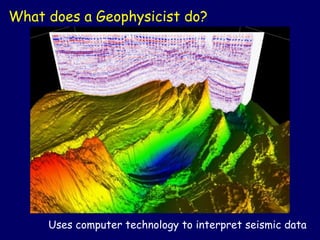
Geophysicists can work both indoors, in an office or lab environment, or outdoors while carrying out fieldwork. Fieldwork can involve being exposed to a variety of climate condition, and possibly unsafe situations, depending upon their area of expertise of the geophysicist. Some geophysicists may likewise invest extended periods of time operating in small teams in remote areas.
When performing fieldwork, the working hours of geophysicists can be long and include nights, weekends and holidays. To end up being a skilled geophysicist, you need to posses a particular set of abilities and personality type. These skills and characteristics will allow you to successfully perform the responsibilities of your task, as well as keep a favorable mindset towards your work.
Geophysical Methods Commonly Employed For Geotechnical ... in Kensington Oz 2022
Institution of higher learnings Federal, provincial/state federal government departments Oil, gas and mining companies Non-profit organizations Geological and geophysical consulting business Public and personal research organizations Our job board listed below has "Geophysicist" postings in Canada, the United States, the UK and Australia, when available:.
Our information suggests that the highest pay for a Geophysicist is $165k/ year Our information indicates that the lowest spend for a Geophysicist is $55k/ year Increasing your pay as a Geophysicist is possible in various methods. Modification of company: Think about a profession transfer to a brand-new company that is prepared to pay higher for your abilities.
Handling Experience: If you are a Geophysicist that supervises more junior Geophysicists, this experience can increase the probability to make more.
Geophysical Prospecting in Beckenham Oz 2020
Physics of the Earth and its area Age of the sea flooring. Much of the dating information comes from magnetic abnormalities. Geophysics () is a topic of life sciences interested in the physical processes and physical properties of the Earth and its surrounding space environment, and making use of quantitative approaches for their analysis.
Geophysics is used to societal requirements, such as mineral resources, mitigation of natural risks and environmental security. In expedition geophysics, geophysical survey information are used to analyze possible petroleum tanks and mineral deposits, find groundwater, discover historical relics, figure out the density of glaciers and soils, and evaluate websites for ecological removal. To supply a clearer idea of what constitutes geophysics, this section explains phenomena that are studied in physics and how they associate with the Earth and its surroundings. Geophysicists also examine the physical processes and properties of the Earth, its fluid layers, and electromagnetic field in addition to the near-Earth environment in the Solar System, that includes other planetary bodies.
The gravitational pull of the Moon and Sun gives increase to two high tides and two low tides every lunar day, or every 24 hr and 50 minutes. There is a space of 12 hours and 25 minutes in between every high tide and in between every low tide. Gravitational forces make rocks push down on deeper rocks, increasing their density as the depth increases.
Geophysicist Salary And Job Description 2023 in Mirrabooka Oz 2023
The surface area gravitational field provides details on the characteristics of tectonic plates. The geopotential surface called the geoid is one meaning of the shape of the Earth. The geoid would be the global mean sea level if the oceans were in balance and might be extended through the continents (such as with very narrow canals).
The main sources of heat are the primitive heat and radioactivity, although there are also contributions from stage shifts. Heat is mainly reached the surface area by thermal convection, although there are 2 thermal boundary layers the coremantle limit and the lithosphere in which heat is transported by conduction. Some heat is carried up from the bottom of the mantle by mantle plumes. If the waves come from a localized source such as an earthquake or surge, measurements at more than one place can be used to locate the source. The areas of earthquakes offer info on plate tectonics and mantle convection. Recording of seismic waves from regulated sources provides details on the area that the waves take a trip through.
Comprehending their systems, which depend on the kind of earthquake (e. g., intraplate or deep focus), can result in much better estimates of earthquake threat and improvements in earthquake engineering. We mainly discover electrical power during thunderstorms, there is constantly a down electrical field near the surface area that averages 120 volts per meter. A variety of electric techniques are utilized in geophysical study., a capacity that emerges in the ground because of man-made or natural disruptions.
Geophysical Survey in Lesmurdie Western Australia 2020
In the extremely conductive liquid iron of the external core, magnetic fields are produced by electrical currents through electro-magnetic induction.
, powering the geodynamo and plate tectonics.
Bs In Physics: Geophysics in Mt Helena Australia 2021
Radioactive components are utilized for radiometric dating, the main approach for establishing an absolute time scale in geochronology. Unsteady isotopes decay at foreseeable rates, and the decay rates of various isotopes cover numerous orders of magnitude, so radioactive decay can be used to accurately date both current events and occasions in past geologic eras.
Fluid movements happen in the magnetosphere, atmosphere, ocean, mantle and core. Even the mantle, though it has an enormous viscosity, flows like a fluid over long time periods. This flow is shown in phenomena such as isostasy, post-glacial rebound and mantle plumes. The mantle circulation drives plate tectonics and the flow in the Earth's core drives the geodynamo.
The rotation of the Earth has extensive results on the Earth's fluid dynamics, typically due to the Coriolis result. In the atmosphere, it generates massive patterns like Rossby waves and figures out the standard circulation patterns of storms. In the ocean, they drive massive circulation patterns as well as Kelvin waves and Ekman spirals at the ocean surface area. The viscosity of rocks is impacted by temperature and pressure, and in turn, determines the rates at which tectonic plates move. Water is a really complicated compound and its unique homes are necessary for life. Its physical homes shape the hydrosphere and are an important part of the water cycle and climate.
Geophysical Surveys - U.s. Geological Survey in Applecross Aus 2020
The numerous types of precipitation involve a complex mix of processes such as coalescence, supercooling and supersaturation. Some precipitated water ends up being groundwater, and groundwater flow includes phenomena such as percolation, while the conductivity of water makes electrical and electro-magnetic approaches useful for tracking groundwater circulation. Physical homes of water such as salinity have a large effect on its motion in the oceans. The Earth is approximately spherical, but it bulges towards the Equator, so it is roughly in the shape of an ellipsoid (see Earth ellipsoid). This bulge is because of its rotation and is nearly constant with an Earth in hydrostatic balance. The detailed shape of the Earth, however, is also affected by the circulation of continents and ocean basins, and to some extent by the dynamics of the plates.
(5. 515) is far higher than the typical particular gravity of rocks at the surface area (2.
3), suggesting that the deeper material is denser. This is also indicated by its low moment of inertia (0. 33 M R2, compared to 0. 4 M R2 for a sphere of consistent density). Some of the density boost is compression under the massive pressures inside the Earth.
Geophysics in Woodvale WA 2023
The conclusion is that pressure alone can not account for the increase in density. Rather, we understand that the Earth's core is composed of an alloy of iron and other minerals. Restorations of seismic waves in the deep interior of the Earth reveal that there are no S-waves in the external core.
The external core is liquid, and the motion of this highly conductive fluid creates the Earth's field. Earth's inner core, nevertheless, is solid since of the enormous pressure. Reconstruction of seismic reflections in the deep interior indicates some significant discontinuities in seismic speeds that demarcate the major zones of the Earth: inner core, external core, mantle, lithosphere and crust.
Table of Contents
- – Geophysicist Bob Embley: Ocean Exploration Ca...
- – Geophysical Survey - Plaza Of The Columns Co...
- – Geology Careers: Degree Requirements, Cost &...
- – Geophysical Methods Commonly Employed For G...
- – Geophysical Prospecting in Beckenham Oz 2020
- – Geophysicist Salary And Job Description 20...
- – Geophysical Survey in Lesmurdie Western Au...
- – Bs In Physics: Geophysics in Mt Helena Aus...
- – Geophysical Surveys - U.s. Geological Surv...
- – Geophysics in Woodvale WA 2023
Latest Posts
Geophysics, Engineering Geophysics And Applied ... in Carmel Western Australia 2023
Airborne Geophysical Surveys Of The Lower Mississippi ... in Balcatta Oz 2022
Working As A Geophysicist And Oceanographer In Canada in Cannington Australia 2023
More
Latest Posts
Geophysics, Engineering Geophysics And Applied ... in Carmel Western Australia 2023
Airborne Geophysical Surveys Of The Lower Mississippi ... in Balcatta Oz 2022
Working As A Geophysicist And Oceanographer In Canada in Cannington Australia 2023